This is a HowTo guide:
To optimize SAP HANA Native Storage Extension (NSE) with partitioning, you need to consider a few key strategies. Here’s a detailed explanation tailored for improving performance and data management using partitioning in combination with NSE:
| Partitioning Strategy | Use partitioning to distribute large tables into smaller, more manageable segments. This can be done based on ranges (range partitioning), list values (list partitioning), or even hash keys (hash partitioning). Partitioning can help in aligning the hot and warm data according to access patterns. For instance, frequently accessed data can be kept in main storage, while less frequently accessed data can be partitioned into NSE. |
| Data Tiering | SAP HANA NSE is designed for effective data tiering, allowing less frequently accessed data to be stored on disk-based storage, reducing memory footprint and costs. You can specify partition-level tiering, where different partitions of the same table can be stored in different storage tiers. This approach is beneficial for handling tables with varying data access patterns across different segments. |
| Partition Pruning | With intelligent partitioning, queries that access only specific partitions allow HANA to perform partition pruning, where only relevant partitions are scanned. This reduces the I/O and processing time significantly, especially beneficial when combined with NSE. Load and Unload Operations: Utilize the capabilities of NSE to manually or automatically unload rarely used partitions to disk and load them back into memory when needed. This operation can be optimized by setting appropriate policies based on usage patterns and business priorities. |
| Indexing on Partitions | Proper indexing strategies on partitions can further enhance access speed. While indexes in HANA are generally memory-resident, consider the impact on performance when indexes for NSE data must be loaded from disk. |
| Monitoring and Adjustments | Regular monitoring of the performance metrics for both the main storage and NSE is crucial. Adjust partitioning and tiering strategies based on changing access patterns and data growth. |
| Combining with Other Features | Combine NSE with features like delta merges, LOB (Large Object) handling, and column store compression to optimize performance and storage further. |
This example describes a HowTo create a SAP HANA RANGE RANGE partition for TABLE EDID4 and unload the table to warm storage with HANA NSE:
# Identification of relevant tables - the enabled NSE Advisor helps you.
ALTER SYSTEM CLEAR CACHE ('cs_access_statistics');
ALTER SYSTEM ALTER CONFIGURATION ('indexserver.ini','system') SET ('cs_access_statistics','collection_enabled') = 'true' WITH RECONFIGURE;
# Verify the recommendations. A good idea is to collect some days of data:
SELECT * FROM SYS.M_CS_NSE_ADVISOR ;
# Range-Range Partitioning of table EDID4
ALTER TABLE .EDID4
PARTITION BY RANGE (MANDT)(
PARTITION VALUE = '000',
PARTITION VALUE = '',
PARTITION VALUE = '',
PARTITION OTHERS ) ,
RANGE (DOCNUM)(
PARTITION '0000000000000000' <= VALUES < '0000000010000000',
PARTITION '0000000010000000' <= VALUES < '0000000020000000',
PARTITION '0000000020000000' <= VALUES < '0000000030000000',
PARTITION '0000000030000000' <= VALUES < '0000000040000000',
PARTITION '0000000040000000' <= VALUES < '0000000050000000',
PARTITION '0000000050000000' <= VALUES < '0000000060000000',
PARTITION '0000000060000000' <= VALUES < '0000000070000000',
PARTITION '0000000070000000' <= VALUES < '0000000080000000',
PARTITION '0000000080000000' <= VALUES < '0000000090000000',
PARTITION '0000000090000000' <= VALUES < '0000000100000000',
PARTITION OTHERS );
# Set EDID4 to page loadable
ALTER TABLE .EDID4 PAGE LOADABLE;
# Unload EDID4
UNLOAD "EDID4" DELETE PERSISTENT MEMORY;
# The DELETE PERSISTENT MEMORY clause is optional and takes care that in context of persistent memory or the fast restart option (SAP Note 2700084) also the main storages are unloaded.
# Disable NSE Advisor if not required anymore
ALTER SYSTEM ALTER CONFIGURATION ('indexserver.ini','system') SET ('cs_access_statistics','collection_enabled') = 'false' WITH RECONFIGURE; 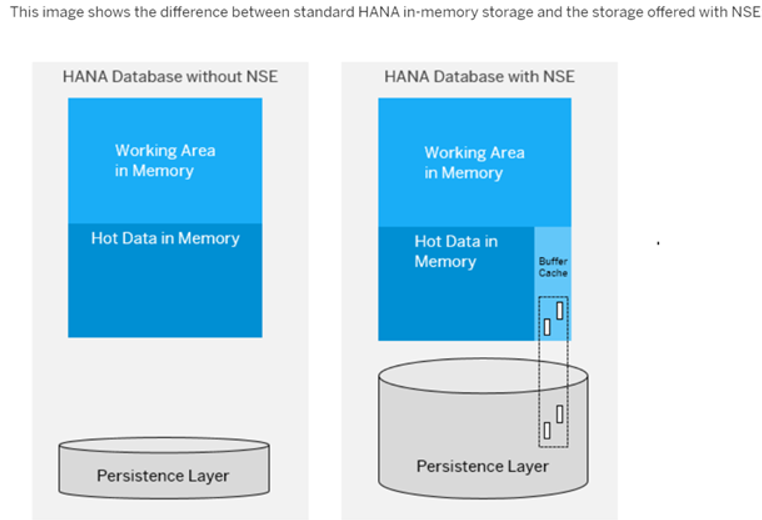
- The HANA column store and row store each have a buffer cache.
- Column loadable data is fully loaded into memory from the disk.
- Page loadable data is loaded from the disk into the buffer cache, page by page as needed.
- Converting column/row loadable data to page loadable format moves the data into the buffer cache.
- When the buffer cache is full, it will eject pages intelligently based on user access patterns.
Warm and hot data are written together from the main store to disk during normal save point operations. The write-optimized store is not paged.
