Dear readers,
Welcome to the latest edition of the DSAG Audit Guide 2023. If you are an auditor, this document is an absolute must-have. In a constantly changing digital world, it is essential to stay up-to-date with technology and the associated auditing standards. The DSAG Audit Guide 2023 is precisely the tool you need for IT auditing. With this guide, spanning 335 pages, you will gain valuable insight into the latest developments and best practices in the field of IT auditing. Whether you want to navigate the depths of SAP S/4HANA compliance or learn about new approaches to effectively auditing cloud applications, this guide is your reliable companion. Each chapter is packed with helpful information and practical instructions that will help you master the most challenging audit tasks with ease and confidence. But that’s not all. The DSAG Audit Guide 2023 is not just a guide; it’s a forum for knowledge exchange where leading auditors and industry experts share their knowledge and experiences.
SAP S/4HANA, the successor to SAP R/3 and SAP ERP, embodies the new generation of SAP’s Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems. Since its inception in 2015, it has been continuously enhanced with novel features and technologies such as analytics and artificial intelligence. The system’s complexity can only be fully leveraged if thorough engagement with audit strategies and security aspects is undertaken.
S/4HANA’s ERP system relies on the underlying HANA database technology. This allows for the modification and simplification of the ERP system’s data model and table structures, leading to rapid data access times and comprehensive real-time analysis. A key component here is the use of SAP HANA’s In-Memory Database (IMDB), which stores data in memory rather than on hard drives, reducing response times.
Audit of the SAP system must consider internal compliance guidelines in addition to legal regulations. In this context, the establishment of auditor roles, which should only display areas relevant to the audit scope, is recommended. In case of special requirements, the emergency user concept should be followed.
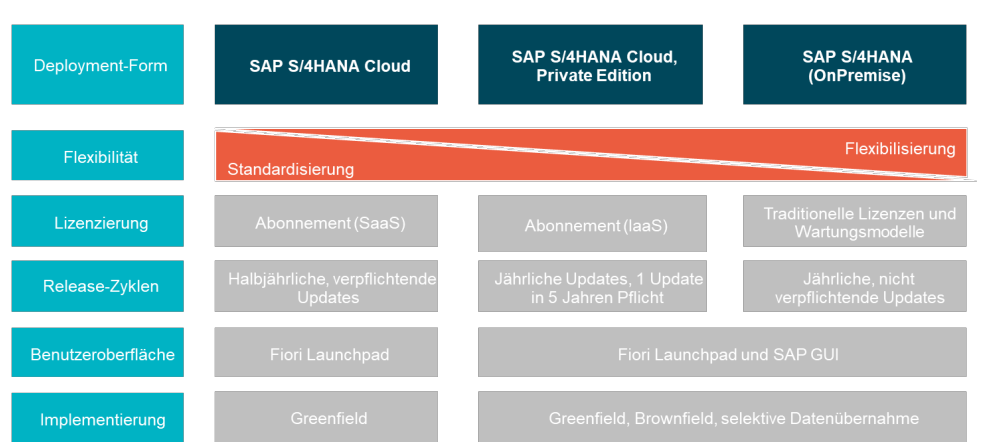
SAP S/4HANA can be operated using various on-premise and cloud options as well as hybrid approaches. The choice of operating model may depend on the company’s IT strategy, functional and legal requirements, innovation needs, and considerations regarding process harmonization and standardization.
For SAP S/4HANA, SAP essentially offers three operating models:
1. SAP S/4HANA (On-premise)
2. SAP S/4HANA Cloud, Private Edition
3. SAP S/4HANA Cloud (SaaS)
All S/4HANA deployment forms are based on the same data model and the SAP HANA database. They vary in terms of standardization and flexibility options, implementation strategy, release cycles, and user interface.
The DSAG Audit Guide, which addresses a multitude of aspects – from authentication and authorization to change management and risk assessment of using SAP GRC, is a crucial companion for the introduction and operation of SAP S/4HANA.
In the context of transitioning to S/4HANA, attention to SAP Security Notes, which are only provided for SAP Support Package Stacks for the last 24 months, is of particular importance. Regularly installing these packages ensures the receipt of appropriate security patches from SAP.
The DSAG test guide is based on the following structure:
A) Authentication
- Introduction
- risks
- control targets
B) Authorization
- Introduction
- risks
- control targets
- Test programs: documentation and standards
- Check programs: roles and authorizations
- Test programs: users and rights
- Test programs: Sensitive functions
- Test programs: functional separation
- Test programs: processes and organization
- Test programs: protocols and parameters
C) Change management with SAP Application Lifecycle Management and Solution Manager
- Introduction
- risks
- control targets
- Test programs: authentication and authorization in change management
- Change management when using S/4HANA Cloud
D) SAP S/4HANA on-premises
- Introduction
- risks
- control targets
- Check programs: authentication
- System parameter settings and security policies
- Check programs: Authorization
- Change management when using SolMan
E) SAP S/4HANA Cloud
- Introduction
- risks
- control targets
- Check programs: Authorization
- Test programs: change management
- Check programs: IT Operation
- Test programs: protocols and parameters
- Audit programs: analysis of the SOC1 type 2 report
F) SAP HANA database
- Introduction
- risks
- control targets
- Check programs: authentication
- Check programs: Authorization
- Test programs: change management
- Check programs: logs and protocols
G) Linux / Unix and Windows operating systems
- Introduction
- risks
- control targets
- Checkers: Unix / Linux system integrity
- Checkers: Windows system integrity
Logging and security monitoring - Data backup, recovery and deletion
H) Risks from the use of SAP GRC
- Access Management Processes
- Adaptation of audit procedures when using SAP GRC Access Control 12
- New IT exam requirements
- Check programs: SAP GRC Access Control
- SoD risks
Which control objectives are there in the SAP audit guide of the DSAG?
Summary of control objectives:
- Ensuring adequate access protection through suitable system parameters and login controls.
- Monitoring and detection of system manipulations through appropriate security policies and audit logs.
- Encryption of communication between client and server according to current procedures.
- Protection of gateway communication using Access Control Lists (ACL).
- Prevention of multiple registrations and definition of validity periods for user IDs.
- Security configurations for special users and mechanisms for managing user groups.
- Monitoring the effectiveness of login controls and installing valid server certificates.
- Establishment of processes for emergency access and auditing of system operations.
- Use of current clients and documentation of the interfaces used.
- Use of single sign-on (SSO).
- Clear definition of control objectives for authorizations and establishment of an effective internal control system and an information security management system (ISMS).
- Effective management of users, roles and permissions, including clear specifications for standard roles and permissions as well as rules for sensitive functions.
- Regular controls and measures for security-related changes, including restrictive assignment of authorizations and separation of development and productive data.
- Clear definition of outsourced services and responsibilities, regular review of the suitability and functionality of the ICS and ensuring the availability of accounting-relevant data.
- Controls to prevent unauthorized access and tampering by the service provider.
- Appropriate database-level authentication and authorization measures to ensure data access only for authorized administrators and technical users.
- Protection of the SAP HANA database and integration of standard IT processes in the S/4 HANA application layer.
How can I get the S4/HANA audit guide from DSAG?
The DSAG (German-speaking SAP user group) provides a variety of guides and resources for its members. This also includes the S/4HANA test guide. Typically, you can obtain these materials from the DSAG website or the DSAG network.
If you are already a member of the DSAG, you can log in to their website and download the guide you want. If you are not a member, you will typically be required to sign up for membership to gain access to full materials and resources.
The guide is available as a PDF here.

